Unlock Word Power: Understanding Prefix Meaning
Have you ever wondered how a tiny addition to the beginning of a word can completely transform its identity and message? It's a fascinating linguistic phenomenon, and at its heart lies the profound concept of "prefix meaning." Prefixes are unsung heroes of language, silently shaping our vocabulary and allowing us to express complex ideas with remarkable precision. They are the building blocks that empower us to create new words, negate existing ones, or indicate subtle relationships of time, place, or manner, making them indispensable tools for effective communication.
Understanding what prefixes are and how they operate is not merely an academic exercise; it's a practical skill that enhances reading comprehension, expands vocabulary, and improves writing clarity. From the simplest words we use daily to the most specialized jargon, prefixes play a pivotal role in conveying precise meanings. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the world of prefixes, exploring their origins, their transformative power, common examples, and how mastering them can unlock a richer understanding of the English language and beyond.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is a Prefix?
- The Etymological Journey of Prefixes
- How Prefixes Transform Meaning
- Common Prefixes and Their Impact
- Prefixes in Action: Real-World Examples
- The Nuance of Hyphenation: When to Use Them
- Beyond English: Prefixes in Other Languages and Fields
- Mastering Prefixes for Enhanced Communication
What Exactly is a Prefix?
At its core, a prefix is a linguistic element—a letter or a group of letters—that is attached to the beginning of a word or a word base to create a new word with a modified meaning. Think of it as a small, powerful key that unlocks a different facet of a word's potential. As the "Data Kalimat" aptly states, "A prefix is a word part that attaches to the beginning of another word or word base to produce a related word or an inflectional form." It's not a standalone word; rather, it's a bound morpheme, meaning it only carries meaning when affixed to another lexical item. The primary function of a prefix is to alter or qualify the meaning of the word it precedes. This alteration can take many forms: it might make the word opposite in meaning, indicate a reversal of action, denote a specific quantity, or even suggest a spatial or temporal relationship. For instance, consider the word "happy." Add the prefix "un-," and it becomes "unhappy," completely reversing its positive connotation. This simple yet profound change highlights the efficiency and elegance of prefixes in language. They are, in essence, compact meaning-modifiers, allowing for a vast expansion of vocabulary without needing entirely new root words for every concept.The Etymological Journey of Prefixes
To truly appreciate the "prefix meaning," it's helpful to understand where these linguistic tools come from. The history of prefixes is deeply rooted in the evolution of language itself, tracing back centuries. According to historical linguistic data, the term "prefix" as a verb emerged in the mid-16th century. Its etymological journey leads us through Old French, specifically "prefixer," which in turn was derived from the Latin "praefixus." The Latin "praefixus" is the past participle of the verb "praefigere," a compound word itself. It breaks down into "prae," meaning "before," and "figere," meaning "to fix." So, "praefixus" literally translates to "fixed in front." This etymological insight perfectly encapsulates the very nature of a prefix: something fixed at the beginning of another element. The noun form of "prefix" followed later, dating from the mid-17th century, derived from the Modern Latin "praefixum," which was the neuter form of "praefixus" used as a noun. This historical context underscores that the concept of "prefix meaning" is not new; it's a linguistic principle that has been recognized and utilized for hundreds of years, evolving as languages themselves evolved. Many of the prefixes we use today have direct Latin or Greek origins, showcasing the enduring influence of classical languages on English vocabulary.How Prefixes Transform Meaning
The power of a prefix lies in its ability to dramatically change the meaning of a word, often with just a few letters. This transformative capacity is one of the most crucial aspects of understanding "prefix meaning." As the provided "Data Kalimat" highlights, "Prefixes can change the meaning of a word, make it negative, or indicate relations of time, place, or manner." This covers a wide spectrum of semantic shifts that prefixes can induce. For example, a common function is negation. Adding "un-" to "do" gives us "undo," meaning to reverse the action. Similarly, "dis-" in "disagree" makes it the opposite of "agree." Beyond simple negation, prefixes can indicate repetition ("re-" in "redo"), a lack of something ("non-" in "non-profit"), or a position ("sub-" in "submarine"). They are incredibly versatile, acting as semantic modifiers that allow for a nuanced expression of ideas.Prefixes and Word Formation
Prefixes are integral to word formation, a process known as derivation. By adding a prefix to an existing word (the root or base word), we create a new word that often belongs to the same part of speech but carries a significantly altered "prefix meaning." For instance, "happy" (adjective) becomes "unhappy" (adjective). "Write" (verb) becomes "rewrite" (verb). This consistency in part of speech is a common characteristic, though not absolute. The ability of prefixes to generate new words from existing ones is a cornerstone of linguistic efficiency. Instead of needing entirely new words for "not happy" or "do again," we simply attach a prefix. This makes language more flexible and adaptable, allowing speakers to coin new terms as needed, often intuitively. The phrase "Adding a prefix to the beginning of an English word changes it to a different word" perfectly encapsulates this fundamental principle of word formation. It's a dynamic process that keeps our language vibrant and expressive.Common Prefixes and Their Impact
To truly grasp "prefix meaning," it's essential to familiarize ourselves with the most common prefixes in English and their typical effects. While the list is extensive, recognizing these frequently encountered prefixes can significantly boost vocabulary and comprehension. Here's a look at some of them, along with their general meanings and examples: * **un-**: Not, opposite of. (e.g., *un*happy, *un*do, *un*pack) * **re-**: Again, back. (e.g., *re*write, *re*turn, *re*build) * **dis-**: Not, opposite of, away. (e.g., *dis*agree, *dis*connect, *dis*appear) * **pre-**: Before. (e.g., *pre*view, *pre*dict, *pre*fix) * **mis-**: Wrongly, badly. (e.g., *mis*understand, *mis*behave, *mis*print) * **non-**: Not. (e.g., *non*-profit, *non*-fiction, *non*-sense) * **in-/im-/il-/ir-**: Not, without. (Forms vary based on the following letter for ease of pronunciation). (e.g., *in*active, *im*possible, *il*legal, *ir*regular) * **sub-**: Under, below. (e.g., *sub*marine, *sub*way, *sub*merge) * **super-**: Above, beyond. (e.g., *super*star, *super*natural, *super*vise) * **anti-**: Against, opposite. (e.g., *anti*social, *anti*biotic, *anti*freeze) * **co-**: With, together. (e.g., *co*-operate, *co*-exist, *co*-pilot) * **ex-**: Out of, former. (e.g., *ex*it, *ex*hale, *ex*-president) * **pro-**: For, forward. (e.g., *pro*gress, *pro*mote, *pro*active) * **de-**: Down, away, reverse. (e.g., *de*scend, *de*activate, *de*frost) * **inter-**: Between, among. (e.g., *inter*national, *inter*net, *inter*act) * **trans-**: Across, beyond. (e.g., *trans*port, *trans*form, *trans*atlantic) * **over-**: Too much, above. (e.g., *over*come, *over*load, *over*look) * **under-**: Too little, below. (e.g., *under*estimate, *under*go, *under*paid) This list, while not exhaustive, provides a solid foundation for recognizing and interpreting the "prefix meaning" in countless words. By understanding these common patterns, one can often deduce the meaning of unfamiliar words, a crucial skill for language acquisition and mastery.Prefixes in Action: Real-World Examples
Seeing prefixes applied in real-world contexts truly illuminates their impact on "prefix meaning." Let's take a few examples to illustrate how these small additions wield significant power: * **"Cycle" vs. "Bicycle" vs. "Tricycle"**: The root "cycle" refers to a wheel or rotation. Adding "bi-" (meaning two) gives us "bicycle," a vehicle with two wheels. Adding "tri-" (meaning three) gives us "tricycle," a vehicle with three wheels. This demonstrates how numerical prefixes precisely define the object. * **"View" vs. "Preview" vs. "Review"**: "View" means to see. "Preview" (pre- meaning before) means to see beforehand. "Review" (re- meaning again) means to see again, often for evaluation. Here, prefixes denote temporal relationships. * **"Agree" vs. "Disagree"**: A straightforward example of negation. "Agree" means to have the same opinion. "Disagree" means to not have the same opinion. * **"Connect" vs. "Disconnect" vs. "Reconnect"**: "Connect" means to join. "Disconnect" means to unjoin or separate. "Reconnect" means to join again. This shows negation and repetition. * **"National" vs. "International"**: "National" refers to a single nation. "International" (inter- meaning between/among) refers to something between or among nations. * **"Fix" vs. "Unfix"**: "Fix" means to make firm or stable. "Unfix" means to undo what was fixed, to detach. This highlights the opposite action. These examples underscore that prefixes are not just arbitrary additions; they are carefully selected linguistic units that convey specific semantic information. Learning to identify them and understand their typical "prefix meaning" is akin to learning a secret code that unlocks a deeper understanding of the English lexicon.The Nuance of Hyphenation: When to Use Them
While understanding the "prefix meaning" is crucial, knowing how to write words with prefixes correctly is equally important for clear communication. One common question arises: when do you use a hyphen with a prefix? The "Data Kalimat" mentions, "See examples of common prefixes and how to write them with or without hyphens." The rules can sometimes seem arbitrary, but there are general guidelines to follow: 1. **Generally, no hyphen:** Most prefixes are attached directly to the root word without a hyphen. * Examples: *unhappy, rewrite, disagree, preview, nonstick, cooperate, submerge*. 2. **When the root word is capitalized:** A hyphen is typically used when the prefix is attached to a proper noun or adjective. * Examples: *un-American, pre-Raphaelite, anti-Bolshevik*. 3. **To avoid awkward double letters:** Sometimes, a hyphen is used to prevent an awkward doubling of the same letter, especially when the prefix ends with the same letter the root begins with. However, this rule is becoming less strict, and many words are now written solid. * Examples (often hyphenated, though some style guides allow solid): *re-elect (re-elect), co-owner (coowner)*. More commonly solid: *unnecessary, cooperate*. 4. **To avoid ambiguity or misreading:** Hyphens are used when their absence would create a word that looks like another word or is difficult to read. * Examples: *re-cover* (to cover again) vs. *recover* (to get well); *re-sign* (to sign again) vs. *resign* (to quit); *un-ionised* (not ionised) vs. *unionised* (formed into a union). 5. **With certain prefixes:** Some prefixes, especially "all-", "ex-" (meaning former), "self-", and "quasi-", almost always take a hyphen. * Examples: *all-inclusive, ex-president, self-aware, quasi-scientific*. 6. **Numerical or letter prefixes:** Prefixes that are numbers or single letters are usually hyphenated. * Examples: *bi-weekly, A-frame, T-shirt, x-ray*. While these guidelines cover most cases, consistency within a document or according to a specific style guide (like APA, MLA, Chicago) is paramount. When in doubt, a quick check with a reputable dictionary is always the best approach to ensure correct usage and maintain clarity in conveying the intended "prefix meaning."Beyond English: Prefixes in Other Languages and Fields
The concept of "prefix meaning" isn't confined to English; it's a universal linguistic phenomenon found in countless languages around the world. Moreover, within specialized fields, prefixes take on very specific and critical roles, often drawing directly from classical roots.Navigating Latin and Greek Roots
As highlighted in the "Data Kalimat," "You are correct, they are from Latin and Greek, we have simply inherited terms from both." Indeed, a vast number of English prefixes, especially those found in scientific, medical, and academic vocabulary, originate directly from Latin and Greek. Understanding these classical roots is like having a master key to unlock the "prefix meaning" of thousands of complex words. For instance, the "Data Kalimat" mentions "Unary, union bi/di meaning two." This directly points to Latin (`uni-` for one, `bi-` for two) and Greek (`di-` for two) numerical prefixes. Consider: * **Latin roots:** `uni-` (one), `bi-` (two), `tri-` (three), `quadri-` (four), `multi-` (many), `omni-` (all), `bene-` (good), `mal-` (bad), `circum-` (around), `contra-` (against). * **Greek roots:** `mono-` (one), `di-` (two), `tri-` (three), `tetra-` (four), `poly-` (many), `eu-` (good), `dys-` (bad), `syn-` (together), `anti-` (against), `hyper-` (over, above), `hypo-` (under, below). These roots are not just academic curiosities; they are living parts of our language. Knowing that "mono-" means one helps us understand "monologue," "monochromatic," and "monopoly." Recognizing "poly-" helps with "polygon," "polyglot," and "polymorphism." The "Data Kalimat" correctly points out, "There is a good reference for Latin and Greek roots over at Wikipedia," underscoring their foundational importance.Specialized Prefixes: Medical and Technical Terms
In fields like medicine, science, and computing, prefixes are not just helpful; they are absolutely essential for precision and clarity. Medical terminology, for instance, is heavily reliant on Latin and Greek prefixes and suffixes to describe body parts, conditions, and procedures. The "Data Kalimat" even references "Medical prefix meaning inner crossword clue," hinting at specific, domain-related prefixes. For example: * **Medical:** `endo-` (inner, within, e.g., *endoscopy*), `exo-` (outer, outside, e.g., *exoskeleton*), `hyper-` (above normal, e.g., *hypertension*), `hypo-` (below normal, e.g., *hypothermia*), `cardio-` (heart, e.g., *cardiology*), `neuro-` (nerve, e.g., *neurology*). * **Computing:** The "Data Kalimat" also mentions "Prefix meaning related to computers crossword clue." While many computing terms use general English prefixes (e.g., *un*install, *re*boot), others draw from Greek/Latin or have specific technical connotations: `cyber-` (computer, e.g., *cybersecurity*), `mega-` (million, e.g., *megabyte*), `giga-` (billion, e.g., *gigabyte*), `nano-` (one billionth, e.g., *nanotechnology*). * **Crossword Clues:** The "Data Kalimat" provides examples like "Prefix meaning new crossword clue" (solution: NEO) and "Prefix meaning Chinese crossword clue" (solution: SINO). These demonstrate how specific prefixes (`neo-` from Greek for new; `Sino-` from Latin for Chinese) are recognized and used to build specific terms (e.g., *neolithic*, *Sinology*). This specialized use of prefixes underscores their role as highly efficient conveyors of complex information within specific domains. For professionals in these fields, a deep understanding of "prefix meaning" is not just an advantage; it's a necessity for accurate communication and comprehension.Mastering Prefixes for Enhanced Communication
The journey to truly master "prefix meaning" is an ongoing one, but the rewards are immense. By consciously recognizing and understanding prefixes, you gain a powerful tool for deciphering unfamiliar words, improving your vocabulary, and enhancing your overall communication skills. It's about moving beyond rote memorization and developing an intuitive grasp of how language builds upon itself. When you encounter a new word, instead of immediately reaching for a dictionary, try to break it down. Does it have a recognizable prefix? If so, what is its common meaning? This analytical approach not only helps you understand the immediate word but also equips you to tackle future vocabulary challenges. For example, knowing that "semi-" means half helps you understand "semicircle," "semifinal," and "semi-automatic." This systematic approach to vocabulary building is far more effective than simply memorizing definitions.The Role of Context in Prefix Meaning
While prefixes generally have consistent meanings, the subtle nuances of "prefix meaning" can sometimes be influenced by context. As the "Data Kalimat" notes, "The difference in meaning is kind of subtle, but it's there." For instance, "de-" can mean "down" (descend), "away" (depart), or "reverse an action" (deactivate). The specific meaning becomes clear within the sentence or phrase. Consider the prefix "in-." It can mean "not" (inactive) or "in/into" (inside). The context of the word and the root it's attached to will clarify which meaning applies. This highlights that while prefixes provide a strong clue, they are part of a larger linguistic system where context always plays a crucial role in determining the precise "prefix meaning" of a word. Developing this contextual awareness is key to becoming a truly proficient language user. In summary, prefixes are not just random letters tacked onto words; they are vital components of language that carry significant semantic weight. Learning what prefixes are, how they change meaning, and how to use them correctly is a fundamental step in achieving linguistic proficiency.In summary, the exploration of "prefix meaning" reveals a foundational aspect of language that empowers us to understand, interpret, and create words with remarkable efficiency. From their ancient Latin and Greek origins to their modern-day application in specialized fields, prefixes are indispensable tools for linguistic precision. They allow us to negate, repeat, indicate quantity, or denote spatial and temporal relationships, transforming root words into a vast array of new terms.
By consciously recognizing common prefixes and their impact, you unlock a powerful method for expanding your vocabulary and enhancing your comprehension skills. This knowledge is not merely academic; it's a practical skill that sharpens your ability to communicate effectively in both written and spoken forms. So, the next time you encounter a new word, take a moment to look for its prefix. You might just uncover a hidden layer of meaning and deepen your appreciation for the intricate beauty of language. What are some of your favorite words that owe their unique meaning to a powerful prefix? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore more of our articles on linguistic insights to continue your journey of language mastery!

PREFIX: 35+ Common Prefixes (with Meaning and Useful Examples) • 7ESL
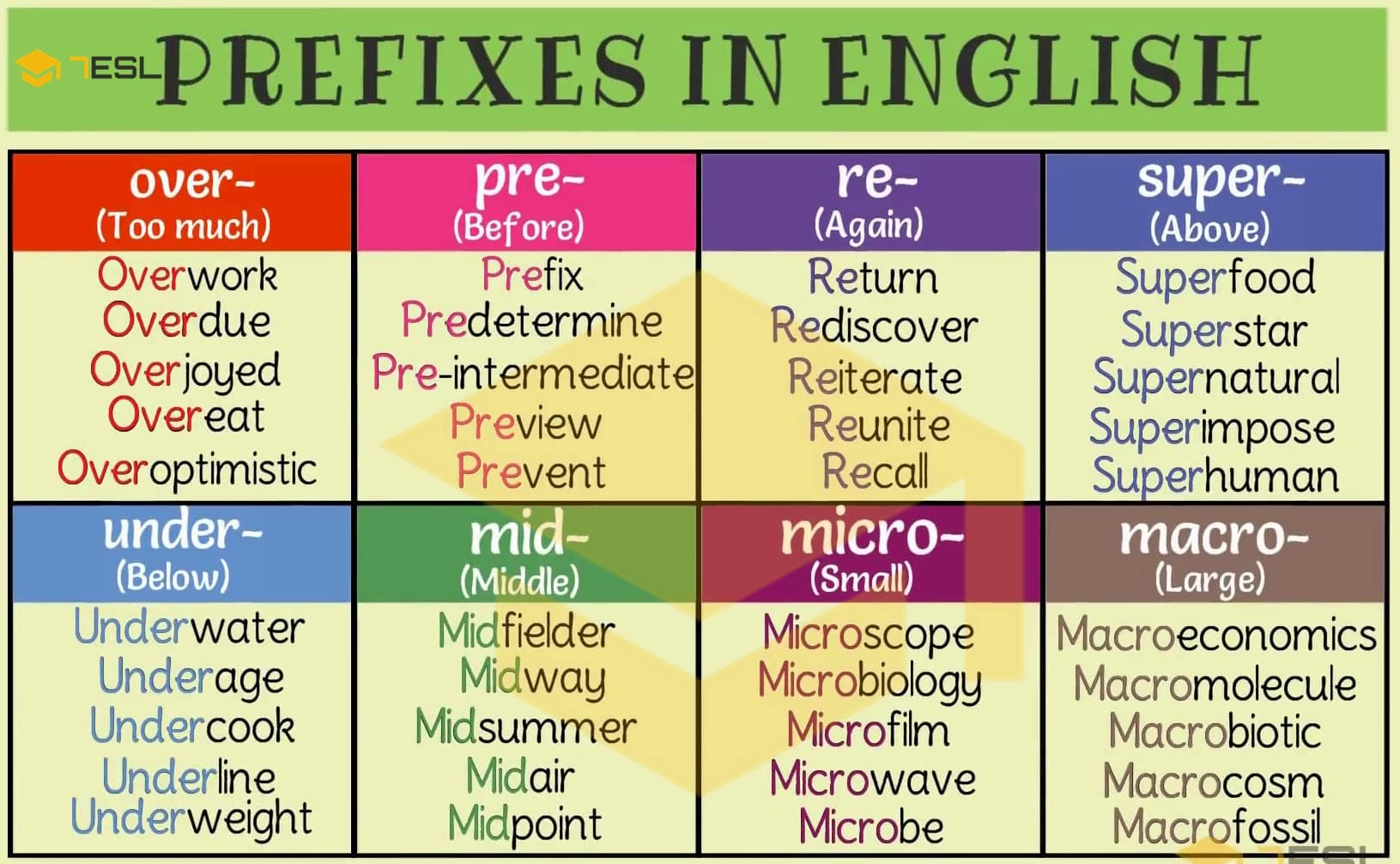
PREFIX: 35+ Common Prefixes (with Meaning and Useful Examples) • 7ESL
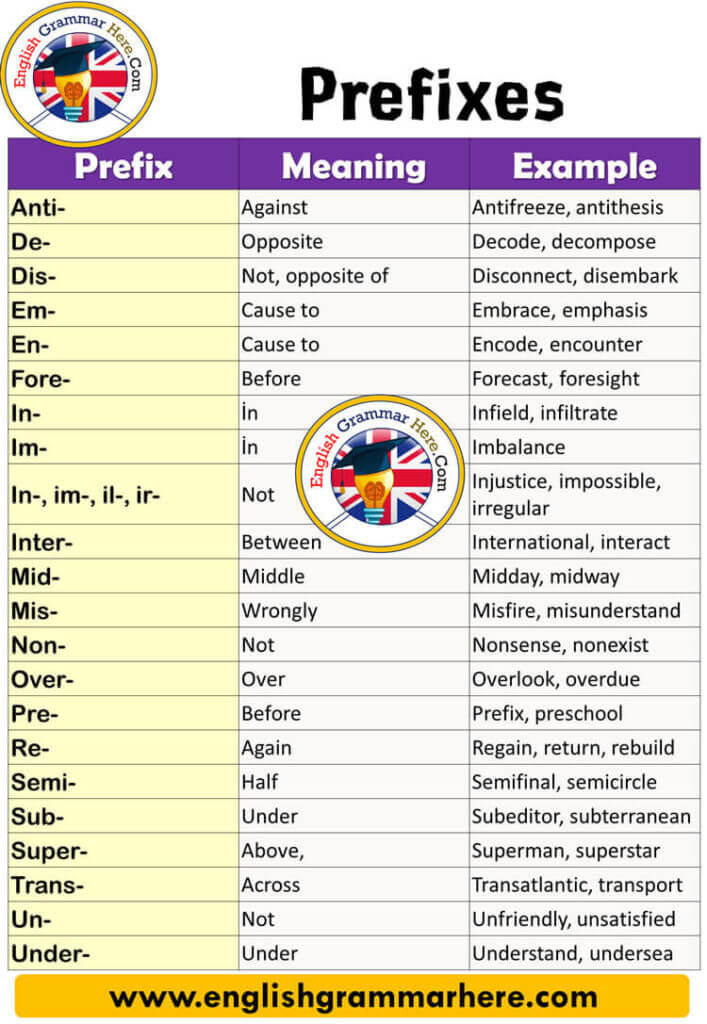
50 Examples of Prefixes, Definition and Examples - English Grammar Here